UKDrugTesting
ALLTEST 10 Parameter URS Urine Cystitis Test Strips Pack Of 100 Test Strips
ALLTEST 10 Parameter URS Urine Cystitis Test Strips Pack Of 100 Test Strips
Couldn't load pickup availability
100 x ALLTEST 10 parameter urine testing strips
You can also buy these urine test strips from our medical supplies website Valuemed
Suitable for testing suspected Ketamine Cystitis and all other kidney, bladder and infection symptoms
- Simple, accurate and easy to use dipstick urine test strips to screen urine for 10 parameters.
- Great value 100 urine test strips per pack.
- Urine test strips for 10 parameter urinalysis ie 10 pad urine tests on each urine test strip for urine health screening.
- Ideal urine test strips for healthcare screening and disease monitoring,
- Give fast, accurate and reliable urine test results.
- Global Brand Urine testing strips manufactured by ALLTEST
- Boxed manufacturers pack with full instructions
- Long expiry date
- Instant results
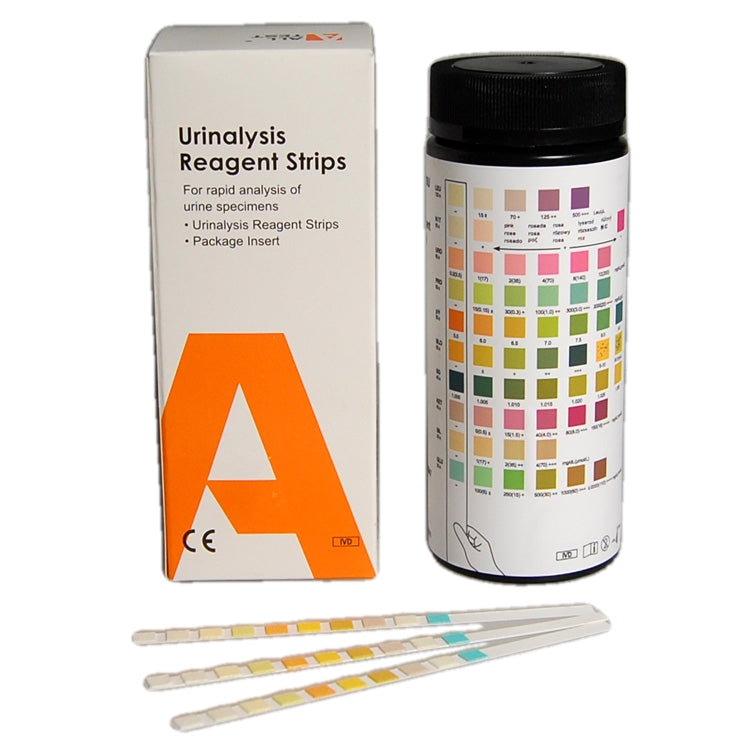
Each test strip tests urine for the following 10 things:
- Glucose
- Ketones
- Specific Gravity
- Blood
- pH
- Protein
- Nitrite
- Bilirubin
- Urobilinogen
- Leucocytes (white blood cells)
Parameters expected to show abnormal results in chemical cystitis (Ketamine) marked in red.
Ketamine cystitis symptoms
Ketamine cystitis is a condition that primarily affects the bladder and urinary tract. The symptoms can vary in severity, but they tend to worsen over time if ketamine use continues. It is important to seek medical attention.
Common symptoms of cystitis include:
- Frequent urination: One of the hallmark signs of cystitis is needing to urinate frequently, often more than 10-20 times per day, even when the bladder isn't full.
- Urgency to pass urine: There is often a sudden, strong urge to urinate, making it difficult to hold urine or delay urination.
- Bladder or pelvic pain: Chronic, dull, or sharp pain in the lower abdomen, bladder, or pelvic region is a common symptom. The pain typically worsens as the bladder fills and may be relieved temporarily after urination.
- Painful urination (Dysuria): Urination can become painful or burning, especially as the bladder becomes inflamed.
- Blood in the urine (Haematuria): Blood may appear in the urine, usually due to bladder wall irritation or ulcers. This could range from visible blood to microscopic amounts detected in a urine test.
- Incontinence: Some individuals experience difficulty controlling their bladder, leading to urine leakage or accidents.
- Nocturia (needing to get up in night to pass urine): Frequent waking at night to urinate, which can disturb sleep patterns, is a common symptom of cystitis.
- Lower back pain: Some people may experience lower back pain, which could indicate issues with the kidneys or be a result of referred pain from bladder inflammation.
- Reduced bladder capacity: Over time, ketamine cystitis can reduce the bladder’s capacity to hold urine, resulting in more frequent trips to the bathroom with smaller amounts of urine being passed.
These symptoms can greatly affect a person’s quality of life and, if left untreated, can lead to chronic bladder damage and potentially irreversible complications. Seeking medical attention early is essential for managing symptoms and preventing long-term bladder problems.
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about ketamine cystitis:
- What is ketamine cystitis? Ketamine cystitis is a condition characterised by bladder inflammation and damage caused by the prolonged or excessive use of ketamine. It leads to symptoms such as frequent urination, pelvic pain, and urinary urgency.
- How does ketamine cause bladder damage? Ketamine and its metabolites are excreted through the urine, where they irritate the bladder lining, causing inflammation, ulcers, and eventually fibrosis. This can result in painful bladder symptoms and reduced bladder capacity.
- What are the early signs of ketamine cystitis? Early symptoms include increased frequency of urination, urinary urgency, pelvic or bladder pain, and occasional blood in the urine. These symptoms often become more severe with continued ketamine use.
- Can ketamine cystitis be reversed? If ketamine use is stopped early enough, some bladder damage may heal over time. However, in advanced cases, bladder damage may be permanent and require ongoing management or surgical intervention.
- How is ketamine cystitis diagnosed? Diagnosis typically involves a medical history review (including drug use), urine tests, and a cystoscopy to look for bladder inflammation or ulcers. In some cases, imaging tests or a bladder biopsy may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
- What are the treatment options for ketamine cystitis? Treatment includes stopping ketamine use, medications to manage symptoms, bladder instillations, and in severe cases, surgical options such as bladder augmentation or removal may be considered. Pelvic floor therapy may also help with pain management.
- How common is ketamine cystitis? It is estimated that up to 30% of regular ketamine users develop some form of bladder damage, including ketamine cystitis, particularly among those who use the drug frequently or in high doses.
- Can you recover from ketamine cystitis completely? Recovery depends on the extent of the damage. Mild cases may improve significantly if ketamine use is stopped, but severe cases can result in permanent bladder dysfunction, even after treatment.
- Is surgery required for ketamine cystitis? Surgery is not always required, but in severe cases where bladder damage is extensive, surgical procedures may be necessary to restore bladder function or alleviate symptoms.
- Can ketamine cystitis lead to other health issues? Yes, aside from bladder damage, chronic ketamine use can affect other organs, including the kidneys (leading to kidney failure), liver, and even the cardiovascular system, increasing risks like high blood pressure and heart issues.
- How can ketamine cystitis be prevented? The most effective way to prevent ketamine cystitis is to avoid using ketamine recreationally.
- Can medical ketamine use cause cystitis? Ketamine used under medical supervision in controlled, therapeutic doses typically does not lead to ketamine cystitis. The condition is more commonly seen in recreational users who take large or frequent doses.
Share
Collapsible content
Have not used them yet but assume all is good.
The urine Alltest 10 parameter kit is so easy to use ,informative and really works well it is a good pack to use multiple times.I will definitely buy this product again.
Great to have at home every time I feel under the weather. Would recommend easy to use and great value


